Almost eight year ago, we first presented a chart first created by JPMorgan's Michael Cembalest, which showed very simply and vividly that reserve currencies don't last forever, and that in the not too distant future, the US Dollar would also lose its status as the world's most important currency, since it is never different this time.
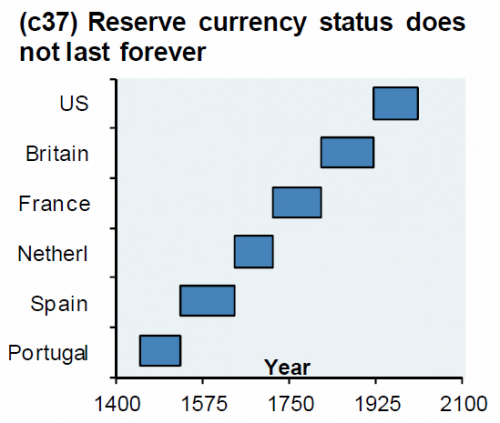
As Cembalest put it back in January 2012, "I am reminded of the following remark from late MIT economist Rudiger Dornbusch: 'Crisis takes a much longer time coming than you think, and then it happens much faster than you would have thought.'"
Perhaps it is not a coincidence then that in light of the growing number of mentions of MMT and various other terminal, destructive monetary policies that have been proposed to kick on the current financial system the can just a little bit longer, that the topic of longevity of reserve currency status is once again becoming all the rage, and none other than JPMorgan's Private Bank ask in this month's investment strategy note whether "the dollar's "exorbitant privilege" is coming to an end?"
So why is JPM, after first creating the iconic chart above which has since spread virally across all financial corners of the internet, not only worried that the dollar's reserve status may be coming to an end, but in fact goes so far as to state that "we believe the dollar could lose its status as the world’s dominant currency (which could see it depreciate over the medium term) due to structural reasons as well as cyclical impediments."
Read on to learn why even the largest US bank has started to lose faith in the world's most powerful currency.
Is the dollar's "exorbitant privilege" coming to an end?
In Brief
The U.S. dollar (USD) has been the world’s dominant reserve currency for almost a century. As such, many investors today, even outside the United States, have built and become comfortable with sizable USD overweights in their portfolios. However, we believe the dollar could lose its status as the world’s dominant currency (which could see it depreciate over the medium term) due to structural reasons as well as cyclical impediments.
Recent data on currency reserve holdings among global central banks suggests this shift may already be under way. As a share of overall central bank reserves, the USD’s role has been declining ever since the Great Recession (see chart). The most recent central bank reserve flow data also suggests that for the first time since the euro’s introduction in 1999, central banks simultaneously sold dollars and bought euros.
Central banks across the globe are also adding to gold reserves at their strongest pace on record. 2018 saw the strongest demand for gold from central banks since 1971 and a rolling four-quarter sum of gold purchases is the strongest on record. To us, this makes sense: gold is a stable source of value with thousands of years of trust among humans supporting it.
Trade Wars have long-term consequences
The current U.S. administration has called into question agreements with nearly all of its largest partners—tariffs on China, Mexico and the European Union, renegotiating NAFTA, as well as abandoning the Trans Pacific Partnership. A more adversarial U.S. administration could also encourage countries to reduce their reliance on USD in trade. Currently 85% of all currency transactions involve the USD despite the U.S. accounting for only roughly 25% of global GDP.
Countries around the world are already developing payment mechanisms that would avoid using the dollar. These systems are small and still developing but this is likely to be a structural story that will extend beyond one particular administration.
No comments:
Post a Comment