“Let no one act as your judge in regard to food or drink or in respect to a festival or a new moon or a Sabbath day things which are a mere shadow of what is to come; but the substance belongs to Christ.” Colossians 2:16-17 (NASB)
This statement by the Apostle Paul refers to the Jewish Feasts as a “mere shadow” of things to come, the substance of them being found in Yeshua, the Messiah. What Paul is saying here is that the feasts were prophetic types, or symbols, that pointed to the Messiah and which would be fulfilled in Him.
Before we pursue that point to see how the feasts were fulfilled in Jesus, let’s first of all familiarize ourselves with the feasts.
Origin and Timing of the Feasts
The feasts were a part of the Mosaic Law that was given to the Children of Israel by God through Moses (Exodus 12; 23:14-17; Leviticus 23; Numbers 28 & 29; and Deuteronomy 16). The Jewish nation was commanded by God to celebrate seven feasts over a seven month period of time, beginning in the spring of the year and continuing through the fall. You will find the timing and sequence of these feasts illustrated on the chart below.
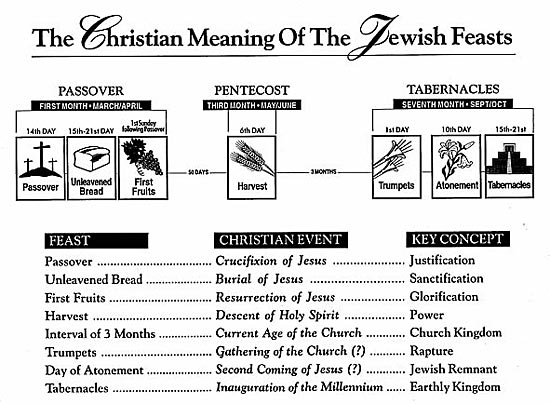
As you study the chart, notice that the feasts fall into three clusters.
The first three feasts Passover, Unleavened Bread, and First Fruits occur in rapid succession in the spring of the year over a period of eight days. They came to be referred to collectively as “Passover.”
The fourth feast, Harvest, occurs fifty days later at the beginning of the summer. By New Testament times this feast had come to be known by its Greek name, Pentecost, a word meaning fifty.
The last three feasts Trumpets, Atonement, and Tabernacles extend over a period of twenty-one days in the fall of the year. They came to be known collectively as “Tabernacles.”
The Nature of the Feasts
Some of the feasts were related primarily to the agricultural cycle. The feast of First Fruits was a time for the presentation to God of the first fruits of the barley harvest. The feast of Harvest was a celebration of the wheat harvest. And the feast of Tabernacles was in part a time of thanksgiving for the harvest of olives, dates, and figs.
Most of the feasts were related to past historical events. Passover, of course, celebrated the salvation the Jews experienced when the angel of death passed over the Jewish houses that were marked with the blood of a lamb. Unleavened Bread was a reminder of the swift departure from Egypt so swift that they had no time to put leaven into their bread.
Although the feasts of Harvest and Tabernacles were related to the agricultural cycle, they both had historical significance as well. The Jews believed that it was on the feast day of Harvest that God gave the Law to Moses on Mt. Sinai. And Tabernacles was a yearly reminder of God’s protective care as the Children of Israel tabernacled in the wilderness for forty years.
The Spiritual Significance of the Feasts
All the feasts were related to the spiritual life of the people.
Passover served as a reminder that there is no atonement for sin apart from the shedding of blood. Unleavened Bread was a reminder of God’s call on their lives to be a people set apart to holiness. Leaven was a symbol of sin. They were to be unleavened that is, holy before the nations as a witness of God.
The feast of First Fruits was a call to consider their priorities, to make certain they were putting God first in their lives. Harvest was a reminder that God is the source of all blessings.
The solemn assembly day of Trumpets was a reminder of the need for constant, ongoing repentance. The Day of Atonement was also a solemn assembly day a day of rest and introspection. It was a reminder of God’s promise to send a Messiah whose blood would cover the demands of the Law with the mercy of God.
In sharp contrast to Trumpets and Atonement, Tabernacles was a joyous celebration of God’s faithfulness, even when the Children of Israel were unfaithful.
The Prophetic Significance of the Feasts
What the Jewish people did not seem to realize is that all of the feasts were also symbolic types. In other words, they were prophetic in nature, each one pointing in a unique way to some aspect of the life and work of the promised Messiah.
1) Passover — Pointed to the Messiah as our passover lamb whose blood would be shed for our sins. Jesus was crucified on the day of preparation for the Passover, at the same time that the lambs were being slaughtered for the Passover meal that evening.
2) Unleavened Bread — Pointed to the Messiah’s sinless life, making Him the perfect sacrifice for our sins. Jesus’ body was in the grave during the first days of this feast, like a kernel of wheat planted and waiting to burst forth as the bread of life.
3) First Fruits — Pointed to the Messiah’s resurrection as the first fruits of the righteous. Jesus was resurrected on this very day, which is one of the reasons that Paul refers to him in I Corinthians 15:20 as the “first fruits from the dead.”
4) Harvest or Pentecost — (Called Shavuot today.) Pointed to the great harvest of souls, both Jew and Gentile, that would come into the kingdom of God during the Church Age. The Church was actually established on this day when the Messiah poured out the Holy Spirit and 3,000 souls responded to Peter’s first proclamation of the Gospel.
The long interval of three months between Harvest and Trumpets pointed to the current Church Age, a period of time that was kept as a mystery to the Hebrew prophets in Old Testament times.
That leaves us with the three fall feasts which are yet to be fulfilled in the life and work of the Messiah.
Because Jesus literally fulfilled the first four feasts and did so on the actual feast days, I think it is safe to assume that the last three will also be fulfilled and that their fulfillment will occur on the actual feast days. We cannot be certain how they will be fulfilled, but my guess is that they most likely have the following prophetic implications:
5) Trumpets — (Called Rosh Hashana today.) Points to the Rapture when the Messiah will appear in the heavens as a Bridegroom coming for His bride, the Church. The Rapture is always associated in Scripture with the blowing of a loud trumpet (I Thessalonians 4:13-18and I Corinthians 15:52)
6) Atonement — (Called Yom Kippur today.) Points to the day of the Second Coming of Jesus when He will return to earth. That will be the day of atonement for the Jewish remnant when they “look upon Him whom they have pierced,” repent of their sins, and receive Him as their Messiah (Zechariah 12:10 and Romans 11:1-6, 25-36).
7) Tabernacles — (Called Sukkot today.) Points to the Lord’s promise that He will once again tabernacle with His people when He returns to reign over all the world from Jerusalem (Micah 4:1-7).
The Week of Millenniums
One final note about the feasts. Six of them the first six are related to man’s sin and struggle to exist.
The last feast, Tabernacles, is related to rest. It is the most joyous feast of the year. It looks to the past in celebration of God’s faithfulness in the wilderness. It looks to the present in celebration of the completion of the hard labor of the agricultural cycle. And it looks to the future in celebration of God’s promise to return to this earth and provide the world with rest in the form of peace, righteousness and justice.
The seven feasts thus parallel what I call the “rhythm of God” that was established during the week of creation namely, six days of work followed by one day of rest.
This rhythm is repeated over and over in the Scriptures, as illustrated in the chart below.
Because God’s division of time into sevens, or weeks, so thoroughly permeates the Scriptures, the Jewish Rabbis concluded before the time of Jesus that human history would extend over a “Week of Millenniums,” or for a period of 7,000 years.
According to the view most frequently expressed in the Talmud, there would be 6,000 years of human toil and strife followed by 1,000 years of peace. This Millennial Sabbath would be the period of the Messianic kingdom during which time the Messiah would reign in person over all the world from Jerusalem (Isaiah 24:21-23).
In other words, the Jews had concluded long before the book of Revelation was written that the Lord’s reign on earth would last a thousand years. Revelation 20 confirmed this deduction by stating six times that the reign would last a thousand years.
The concept of the Millennium in the book of Revelation is therefore nothing new. The concept is rooted in the creation week of Genesis. It is reaffirmed in the week of feasts of Israel six feasts related to sin and toil leading up to a sabbath feast of rest.
As you can see from the chart below, we are near the end of the 6,000 years which the Jewish Rabbis believed would usher in the Millennial kingdom. We are standing on the threshold of the Sabbath Millennium. Yeshua is coming soon!
The way in which Jesus fulfilled the Jewish feasts is a fascinating study. In the Hebrew Scriptures, the Jewish prophet Amos records that God declared He would do nothing without first revealing it to His servants, the prophets (Amos 3:7). From the Old Covenant to the New, Genesis to Revelation, God provides picture after picture of His entire plan for mankind and one of the most startling prophetic pictures is outlined for us in the Jewish feasts of Leviticus 23.
The Hebrew word for “feasts” (moadim) literally means "appointed times." God has carefully planned and orchestrated the timing and sequence of each of these seven feasts to reveal to us a special story. The seven annual feasts of Israel were spread over seven months of the Jewish calendar, at set times appointed by God. They are still celebrated by observant Jews today. But for both Jews and non-Jews who have placed their faith in Jesus, the Jewish Messiah, these special days demonstrate the work of redemption through God’s Son.
The first four of the seven feasts occur during the springtime (Passover, Unleavened Bread, First Fruits, and Weeks), and they all have already been fulfilled by Christ in the New Testament. The final three holidays (Trumpets, the Day of Atonement, and Tabernacles) occur during the fall, all within a short fifteen-day period.
Many Bible scholars and commentators believe that these fall feasts have not yet been fulfilled by Jesus. However, the “blessed hope” (Titus 2:13) for all believers in Jesus Christ is that they most assuredly will be fulfilled. As the four spring feasts were fulfilled literally and right on the actual feast day in connection with Christ's first coming, these three fall feasts, it is believed by many, will likewise be fulfilled literally in connection to the Lord's second coming.
In a nutshell, here is the prophetic significance of each of the seven Levitical feasts of Israel:
1) Passover (Leviticus 23:5) – Pointed to the Messiah as our Passover lamb (1 Corinthians 5:7) whose blood would be shed for our sins. Jesus was crucified on the day of preparation for the Passover at the same hour that the lambs were being slaughtered for the Passover meal that evening (John 19:14).
2) Unleavened Bread (Leviticus 23:6) – Pointed to the Messiah's sinless life (as leaven is a picture of sin in the Bible), making Him the perfect sacrifice for our sins. Jesus' body was in the grave during the first days of this feast, like a kernel of wheat planted and waiting to burst forth as the bread of life.
3) First Fruits (Leviticus 23:10) – Pointed to the Messiah's resurrection as the first fruits of the righteous. Jesus was resurrected on this very day, which is one of the reasons that Paul refers to him in 1 Corinthians 15:20 as the "first fruits from the dead."
4) Weeks or Pentecost (Leviticus 23:16) – Occurred fifty days after the beginning of the Feast of Unleavened Bread and pointed to the great harvest of souls and the gift of the Holy Spirit for both Jew and Gentile, who would be brought into the kingdom of God during the Church Age (see Acts 2). The Church was actually established on this day when God poured out His Holy Spirit and 3,000 Jews responded to Peter's great sermon and his first proclamation of the gospel.
5) Trumpets (Leviticus 23:24) – The first of the fall feasts. Many believe this day points to the Rapture of the Church when the Messiah Jesus will appear in the heavens as He comes for His bride, the Church. The Rapture is always associated in Scripture with the blowing of a loud trumpet (1 Thessalonians 4:13-18 and 1 Corinthians 15:52).
2) Unleavened Bread (Leviticus 23:6) – Pointed to the Messiah's sinless life (as leaven is a picture of sin in the Bible), making Him the perfect sacrifice for our sins. Jesus' body was in the grave during the first days of this feast, like a kernel of wheat planted and waiting to burst forth as the bread of life.
3) First Fruits (Leviticus 23:10) – Pointed to the Messiah's resurrection as the first fruits of the righteous. Jesus was resurrected on this very day, which is one of the reasons that Paul refers to him in 1 Corinthians 15:20 as the "first fruits from the dead."
4) Weeks or Pentecost (Leviticus 23:16) – Occurred fifty days after the beginning of the Feast of Unleavened Bread and pointed to the great harvest of souls and the gift of the Holy Spirit for both Jew and Gentile, who would be brought into the kingdom of God during the Church Age (see Acts 2). The Church was actually established on this day when God poured out His Holy Spirit and 3,000 Jews responded to Peter's great sermon and his first proclamation of the gospel.
5) Trumpets (Leviticus 23:24) – The first of the fall feasts. Many believe this day points to the Rapture of the Church when the Messiah Jesus will appear in the heavens as He comes for His bride, the Church. The Rapture is always associated in Scripture with the blowing of a loud trumpet (1 Thessalonians 4:13-18 and 1 Corinthians 15:52).
6) Day of Atonement (Leviticus 23:27) – Many believe this prophetically points to the day of the Second Coming of Jesus when He will return to earth. That will be the Day of Atonement for the Jewish remnant when they "look upon Him whom they have pierced," repent of their sins, and receive Him as their Messiah (Zechariah 12:10 and Romans 11:1-6, 25-36).
7) Tabernacles or Booths (Leviticus 23:34) – Many scholars believe that this feast day points to the Lord's promise that He will once again “tabernacle” with His people when He returns to reign over all the world (Micah 4:1-7).
7) Tabernacles or Booths (Leviticus 23:34) – Many scholars believe that this feast day points to the Lord's promise that He will once again “tabernacle” with His people when He returns to reign over all the world (Micah 4:1-7).
Should Christians celebrate these Levitical feast days of Israel today? Whether or not a Christian celebrates the Jewish feast days would be a matter of conscience for the individual Christian. Colossians 2:16-17 tells us, “Therefore do not let anyone judge you by what you eat or drink, or with regard to a religious festival, a New Moon celebration or a Sabbath day. These are a shadow of the things that were to come; the reality, however, is found in Christ.” Christians are not bound to observe the Jewish feasts the way an Old Testament Jew was, but we should not criticize another believer who does or does not observe these special days and feasts (Romans 14:5).
While it is not required for Christians to celebrate the Jewish feast days, it is beneficial to study them. Certainly, it could be beneficial to celebrate these days if it leads one to a greater understanding and appreciation for Christ’s death and resurrection and the future promise of His coming. As Christians, if we choose to celebrate these special days, we should put Christ in the center of the celebration, as the One who came to fulfill the prophetic significance of each of them.
No comments:
Post a Comment